SEAStAR
SEAStAR tools version 0.5.0 has been released on github.
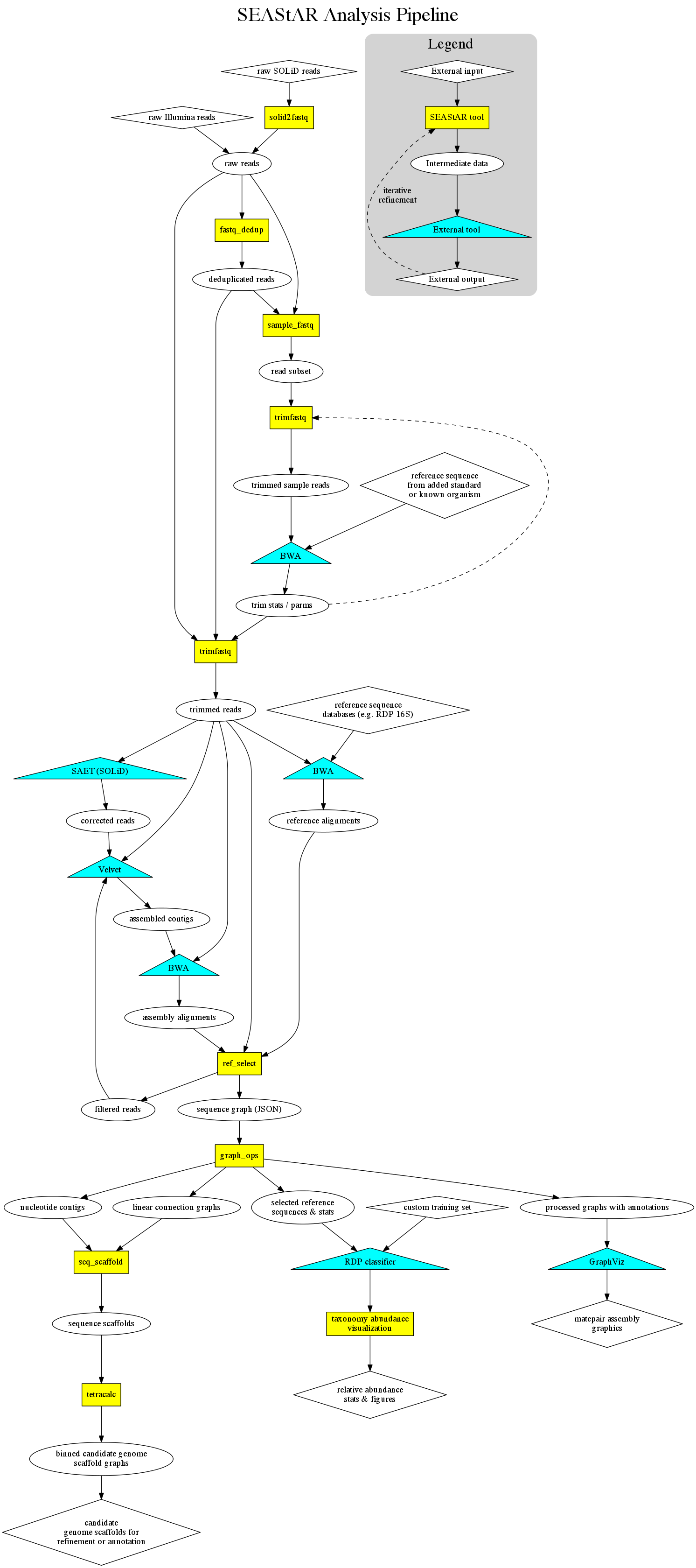
SEAStAR is a package of open-source tools supporting the construction of analysis pipelines for environmental next-generation sequencing data. Version 0.4 includes new support for Illumina® reads in addition to SOLiD™ data, and provides high-performance tools for dealing with:
- Converting between file formats (CSFASTA -> FASTQ)
- Trimming raw reads for quality (with tuning support)
- PCR de-duplication of paired reads (without reference sequences)
- Selecting and estimating the relative abundance of sequences from large reference databases (e.g. 16S rDNA)
- Sub-sampling paired FASTQ files randomly, or based on reads included in (or excluded from) reference alignments
- Converting assembled color-space (SOLiD) contigs to nucleotide-space
- Connecting assembled contigs together via paired reads (constructing an assembly graph)
- Splitting complicated metagenomic assembly graphs into well-supported scaffolds
- Binning scaffolds by organism using tetra-nucleotide statistics
- Identifying small circular scaffolds that are likely virus or plasmid genomes
The prototype version of SEAStAR was developed and used to analyze the metagenome data in our publication: “Untangling Genomes from Metagenomes: Revealing an Uncultured Class of Marine Euryarchaeota”.
It was also used extensively for the analysis in Vaughn Iverson’s 2015 Ph.D. dissertation “Untangling Genomes from Metagenomes”.
SEAStAR was publicly released in the following phases (versions prior to 0.3 were prototypes):
Phase 1 (ver 0.3):
Phase 1 contained tools developed for working with SOLiD reads, converting them to colorspace FASTQ files, removing PCR duplicates, and trimming the reads based on quality and information content for various uses. These tools generate files that can be directly used with aligners and assemblers, such as BWA and Velvet.
Phase 2: (ver 0.4)
Phase 2 added support for Illumina sequence, and contains the tools we developed for processing SAM alignment files and assembled nucleotide or colorspace contigs into mate-paired assembly graphs with associated nucleotide contigs that can then be visualized and explored using GraphViz. This release also contains the tools for selecting and visualizing the best sequences from a reference database (e.g. the RDP 16S database) alignment with associated statistics such as coverage and relative abundance. In the case of alignments with RDP, these sequences can then be classified (using the RDP classifier) and visualized taxonomically. Also included are tools for splitting assembly graphs into parsimonious linear scaffold graphs, binning these scaffold graphs using tetra-nucleotide statistics, and constructing scaffold sequences with the order and orientation of contigs properly determined. Use of this full pipeline produces candidate genome assemblies ready for refinement, gap-filling (if desired) and annotation.
Phase 3: (ver 0.5)
Adds support for identifying, isolating and reassembling topologically circular (virus and plasmid) scaffold sequences.
Thanks for your interest in the SEAStAR tools, we hope you enjoy using them. – Vaughn Iverson and Chris Berthiaume